Last week, our President, Dr. Brandon Roberts, PhD, spoke on three different topics central to understanding and addressing fair lending risk management in today’s environment.
From the changing regulatory landscape to specifics on gathering, maintaining, and understanding lending data to the imminent implications of SB 1071, read on for a recap and resources to learn more.
New Wine – Old Wine Bottles | Embracing the New Paradigm for Fair Lending Risk Management
The session discussed the evolving landscape of fair lending risk management, highlighting significant changes in regulatory expectations and the need for robust risk management practices. Here are some of the highlights:
- Changing Regulatory Landscape: The regulatory environment for banks has changed dramatically, with a greater focus on fair lending in examinations, especially for larger banks.
- Unmanaged Risks: Many banks have a lot of unmanaged risks they are unaware of, making prevention crucial since there is no cure for fair lending issues.
- Increased Documentation and Knowledge: Regulators now require more documentation and expect compliance teams to be highly knowledgeable about the lending function.
- Deeper Examinations: Examinations have become more granular, focusing on subtleties and inconsistencies, and take longer to complete.
- Reliance on Data and Statistics: The approach to fair lending has become increasingly data-driven, with large banks expecting statistical analyses during exams.
- Lower Bar for Discrimination: The burden of proof for showing discrimination has been lowered, making it easier for regulators to identify patterns or practices of discrimination.
- Impact on Mergers and Acquisitions: Fair lending concerns are now given more weight in merger and acquisition activities, potentially influencing outcomes.
- Board Involvement: There is an increased expectation for direct involvement from the Board in managing fair lending risks, despite challenges like limited time and complexity.
- Dominant Concerns: Top fair lending concerns include redlining, exceptions, discretion, and underwriting, each with specific risk factors and implications.
- Understanding Statistics: Compliance and risk managers must understand basic statistical concepts to effectively communicate risks and findings to executive management and the Board.
The Datasphere – Navigating Data-Driven Compliance
The session discussed the evolution and implications of data-driven approaches to fair lending analysis, emphasizing the importance of data integrity and the increasing regulatory expectations.
- Historical Context: Fair lending analysis using statistical methods began in the late 1990s, with significant developments in the early 2000s when agencies started using regression and statistics to identify discrimination.
- Past Fair Lending Reviews: Previously, fair lending reviews were manual, labor-intensive, and subjective, with limited scope and smaller sample sizes.
- Data-Driven Regulatory Approach: The shift to a data-driven approach has made fair lending analysis more empirical, definitive, and capable of evaluating a wider scope of data.
- Challenges with Data: Many institutions face challenges with data availability, integrity, and management, making it difficult to conduct effective fair lending analysis.
- Regulatory Expectations: Regulatory expectations are increasing for all banks, with larger banks facing higher scrutiny and the need for comprehensive data analysis.
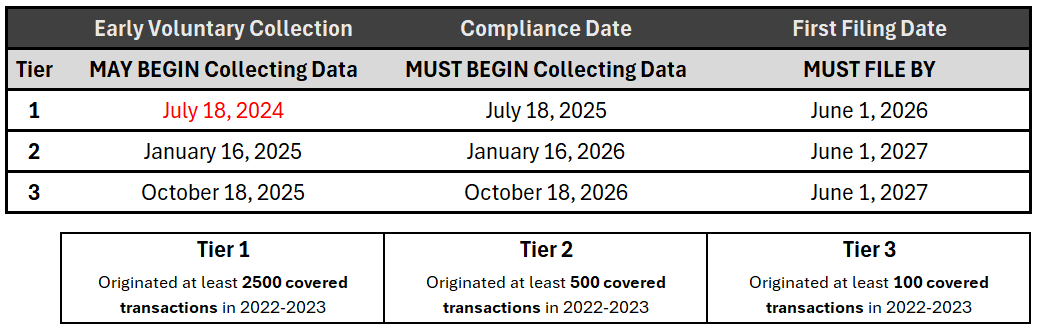
- Role of 1071 Reporting: The implementation of Section 1071 reporting will add complexity to fair lending risk management, requiring timely and thorough data analysis.
- Technological Advancements: Advancements in technology, data science, AI, and machine learning will further increase the reliance on data for fair lending analysis.
- Steps for Compliance: Banks should define and quantify policies, inventory current data, identify data sources, plan data management, and secure management buy-in to ensure effective fair lending compliance.
Small Business Reporting Under Section 1071 – A Deep Dive
The session dives into the details of Section 1071 of the Dodd-Frank Act, focusing on small business lending data collection and its implications.
- Dodd-Frank Act Overview: Section 1071 of the Dodd-Frank Act amends the Equal Credit Opportunity Act to mandate financial institutions to collect and submit data on credit applications from women-owned, minority-owned, and small businesses.
- Role of the CFPB: The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) was created by the Dodd-Frank Act and is responsible for implementing Section 1071. This agency focuses solely on consumer protection and compliance.
- Purpose of Section 1071: Section 1071 aims to facilitate fair lending law enforcement and help identify business and community development needs for women-owned, minority-owned, and small businesses.
- Reporting Requirements: Banks must report data if they have originated at least 100 small business loans in each of the two preceding years. The data collected will be used to monitor and enforce fair lending practices.
- Fair Lending Implications: The 1071 rule has significant fair lending implications, requiring banks to be aware of potential risks associated with the data they collect and report.
- Challenges and Risks: Small business lending is largely unmonitored for fair lending risks, and the implementation of 1071 will add significant compliance burdens and risks.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning technologies can help manage the vast amounts of data required for compliance but also introduce new risks and require careful monitoring.
- Future of Data Analysis: With the increase in publicly available data, AI and ML models may identify patterns of discrimination or bias in lending practices that traditional methods might miss.
- Next Steps for Banks: Banks need to adopt a holistic approach to fair lending risk management, focusing on timely analyses and a data-driven approach to stay ahead of potential risks.
General Resources
Fair Lending Examination Procedures:
https://www.ffiec.gov/pdf/fairlend.pdf
Redlining in an exam context:
https://www.fdic.gov/resources/bankers/fair-lending/documents/fdic-redlining-fair-lending-resources-page.pdf
Special Purpose Credit Products:
https://www.fdic.gov/news/financial-institution-letters/2022/fil22008.html
Guidance concerning DOJ referrals:
https://www.justice.gov/sites/default/files/crt/legacy/2014/03/05/regguide.pdf
Analysis of HMDA Data:
https://www.fdic.gov/bank-examinations/hmda-data-identifying-and-analyzing-outliers
Regression Analysis:
https://www.premierinsights.com/blog/on-the-use-of-regression-analysis-in-fair-lending
SB 1071 Resources
Links to most information can be found here:
https://www.consumerfinance.gov/1071-rule/
Reporting resources:
https://www.consumerfinance.gov/data-research/small-business-lending/
Timetable for Reporters: